Intel Chipsets Get the essential features you need—from the data center to the network edge. Choose chipsets for extreme power and performance, for consumers and enthusiasts, or for the enterprise. The H61 was released without too much fuss a while ago. As with previous, lower-end chipsets (the G31, and G41), it seems that Intel is trying to extend the reach of their new processors by providing a cheaper platform for their new Sandy Bridge family of CPUs. LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is a socket used for Intel microprocessors based on Sandy Bridge(2k) and Ivy Bridge(3k) microarchitectures.It was designed as a replacement for LGA 1156 (known as Socket H).
- Intel H61 Motherboard Specs
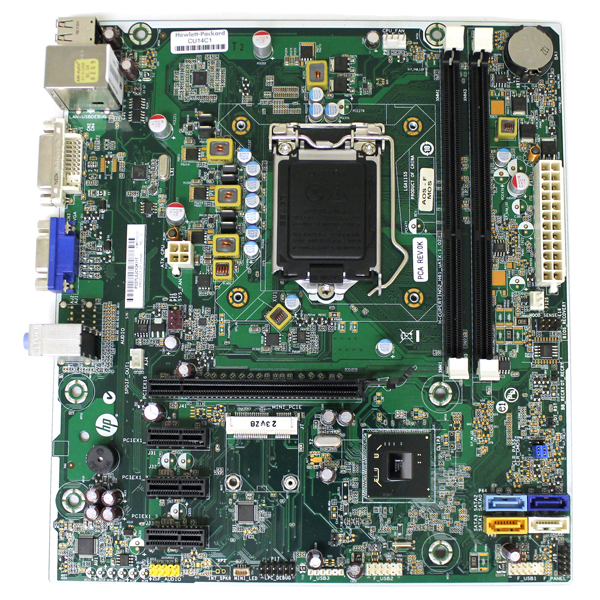
- Intel H61 Motherboard Specs
- Motherboard H61m-p23 (b3) Intel H61 Chipset
- Intel H61 Drivers
| Type | LGA |
|---|---|
| Processor dimensions | 37.5 × 37.5 mm2[1] |
| Processors | Sandy Bridge, Ivy Bridge |
| Predecessor | LGA 1156 |
| Successor | LGA 1150 |
| Memory support | DDR3 |
| This article is part of the CPU socket series | |
LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is a socket used for Intelmicroprocessors based on Sandy Bridge (2nd-Gen, 32nm, 2k-series) and Ivy Bridge (3rd-Gen, 22nm, 3k-series) microarchitectures.
It is the successor of LGA 1156 (known as Socket H) and was itself succeeded by LGA 1150 in 2013.
LGA 1155 has 1155 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The pins are arranged in a 40×40 array with a 24×16 central void and additional 61 omitted pins (two adjoining the central void, six in each of the four corners, and 35 in groups around the perimeter), yielding the 1600 − 384 − 61 = 1155 pin count. Processors for LGA 1155 and LGA 1156 sockets are not compatible with each other since they have different socket notches.
LGA 1155 also marked the beginning of secure boot with support in some later boards.
Heatsink[edit]
The 4 holes for fastening the heatsink to the motherboard are placed in a square with a lateral length of 75 mm for Intel's sockets LGA 1156, LGA 1155, LGA 1150 and LGA 1151. Cooling solutions should therefore be interchangeable.
Cooling systems are compatible between LGA 1155 and LGA 1156 sockets, as the processors have the same dimensions, profile and construction, and similar levels of heat production.[2]
Sandy Bridge family of chipsets[edit]
Sandy Bridge chipsets, except B65, Q65 and Q67, support both Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge CPUs through a BIOS upgrade.[3] Sandy Bridge based processors officially support up to DDR3-1333 memory, however in practice speeds up to DDR3-2133 have been tested to work successfully.[4]
The H61 chipset only supports one double-sided DIMM Memory module (RAM module) per memory-channel and therefore is limited to 16 GB instead of the 32 GB like the others support.[5] On H61-based motherboards with four DIMM slots, only four single-sided DIMMs can be installed.[6]
| Name[7] | H61 | B65 | Q65 | Q67 | H67[8] | P67 | Z68[9] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overclocking | GPU | CPU + RAM | CPU + GPU + RAM | ||||
| Allows using built-in GPU with Intel Clear Video Technology | Yes | No | Yes | ||||
| Maximum USB 2.0 ports[a] | 10 | 12 | 14 | ||||
| Maximum SATA 2.0/3.0 ports | 4 / 0 | 4 / 1 | 4 / 2 | ||||
| Main PCIe configuration | 1 × PCIe 2.0 ×16 |
| |||||
| Secondary PCIe | 6 × PCIe 2.0 ×1 | 8 × PCIe 2.0 ×1 | |||||
| Conventional PCI support[b] | No | Yes | No | ||||
| Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RAID) | No | Yes | |||||
| Smart Response Technology | No | Yes | |||||
| Ivy Bridge processor support | Yes | No | Yes | ||||
| Intel Active Management, Trusted Execution, Anti-Theft, and vPro Technology | No | Yes | No | ||||
| Release date | February 2011 | May 2011 | January 2011 | May 2011 | |||
| Maximum TDP | 6.1 W | ||||||
| Chipset lithography | 65 nm | ||||||
Ivy Bridge family of chipsets[edit]
All Ivy Bridge chipsets and motherboards support both Sandy Bridge and Ivy Bridge CPUs. Ivy Bridge based processors will officially support up to DDR3-1600, up from DDR3-1333 of Sandy Bridge. Some consumer Ivy Bridge chipsets will also allow overclocking of K-series processors.[10]
| Name[11] | B75 | Q75 | Q77 | H77 | Z75 | Z77 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overclocking | CPU (Bclk) + GPU | CPU + GPU + RAM | ||||
| Allows using built-in GPU | Yes | |||||
| Intel Clear Video Technology | Yes | |||||
| RAID | No | Yes | ||||
| Maximum USB 2.0/3.0 ports | 8 / 4 | 10 / 4 | ||||
| Maximum SATA 2.0/3.0 ports | 5 / 1 | 4 / 2 | ||||
| Main PCIe configuration[c] | 1 × PCIe 3.0 ×16 |
| ||||
| Secondary PCIe | 8 PCIe 2.0 ×1 | |||||
| Conventional PCI[b] | Yes | No [12] | ||||
| Intel Rapid Storage Technology | No | Yes | ||||
| Intel Anti-Theft Technology | Yes | |||||
| Smart Response Technology | No | Yes | No | Yes | ||
| Intel vPro | No | Yes | No | |||
| Release date | April 2012[13] | |||||
| Maximum TDP | 6.7 W | |||||
| Chipset lithography | 65 nm[14] | |||||
NVMe[edit]
A PCGHX user[who?] wrote an article on the website de:PC Games Hardware describing how to take UEFI modules from some Z97 motherboards and use them with an Z77-motherboard to make the later support booting from an SSD using the NVM Express protocol, instead of the AHCI protocol.[15] That article claims, the Z97 motherboards were the first to officially and fully support the NVMe protocol.
Intel H61 Motherboard Specs
'Als Erstes gilt es die fraglichen Module aus einem möglichst ähnlichen BIOS der Z97-Generation zu extrahieren. Dies ist die erste Generation von Mainboards, die NVMe-Laufwerke nativ unterstützt.'
The mods described also work with B75 Chipset motherboards.
Notes[edit]
Intel H61 Motherboard Specs


- ^USB 3.0 is not supported by any of these chipsets. Motherboard manufacturers may use external hardware to add USB 3.0 support.
- ^ abAlthough some of the chipsets do not support conventional PCI, motherboard manufacturers may include support through the addition of third-party PCI bridges.
- ^For PCIe 3.0 capability, the Ivy Bridge CPU must have the relevant PCIe 3.0 controller built in. However, some Ivy Bridge CPUs only have a PCIe 2.0 controller built in.
References[edit]
Motherboard H61m-p23 (b3) Intel H61 Chipset
- ^'Intel Core 2 gen CPUs and Socket 1155 Datasheet'(PDF).
- ^'2nd Gen Intel Core Processor, LGA1155 Socket:'(PDF). Download.intel.com. Archived from the original(PDF) on 2011-07-13. Retrieved 2012-09-26.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^'Ivy Bridge Quad-Core to Have 77W TDP, Intel Plans for LGA1155 Ivy Bridge Entry'. techPowerUp. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ^'Sandy Bridge Memory Scaling: Choosing the Best DDR3'. AnandTech. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ^'Intel H61 Express Chipset'. Intel.com. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ^'Motherboards- ASUS P8H61 EVO'. ASUS. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ^'ARK - Compare Intel Products'. Intel ARK (Product Specs).
- ^'Intel H67 Express Chipset'. Intel.com. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ^'Intel SSD Caching Feature for Z68 Chipset Explored'. Vr-zone.com. 2011-04-25. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ^'Intel's Roadmap: Ivy Bridge, Panther Point, and SSDs'. AnandTech. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ^'ARK - Compare Intel Products'. Intel ARK (Product Specs).
- ^'Intel 7 Series Chipset Family PCH: Datasheet'. Intel.com. Retrieved 2014-12-02.
- ^'Intel 7-Series Chipset Officially Debuts, Derived Desktop Board Products Launched'. techPowerUp. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ^'ARK | Intel Z77 Express Chipset (Intel BD82Z77 PCH)'. Ark.intel.com. Retrieved 2012-09-26.
- ^'Booten von einer NVMe-SSD'. 2016-10-13.